Affiliate Disclosure
HVAC Guide Guys is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.
How Do Modern HVAC Systems Work? HVAC systems filter and purify the air, which improves indoor air quality. Modern HVAC systems ensure comfortable and healthful indoor settings by controlling airflow and minimizing energy usage. Let’s look at how these systems work and the advantages they provide in terms of energy efficiency and general comfort.
Modern HVAC systems work by circulating refrigerant between interior and outdoor units, efficiently transferring heat and cooling the air. These systems regulate temperature and humidity levels within buildings by combining components such as compressors, coils, and fans.
Table of Contents
Introduction To Modern Hvac Systems
Modern HVAC systems are critical to ensuring maximum comfort and a healthy indoor environment. Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems have advanced significantly in terms of efficiency and functionality. In this blog post, we’ll look at the key components of modern HVAC systems and highlight some recent innovations that have transformed how we manage our indoor climate.
Essential Components
Modern HVAC systems are made up of numerous key components that work together to provide effective heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. These components include:
- Air Handler: The air handler circulates conditioned air throughout the structure. Its components include a blower, filters, and a heat exchanger or cooling coil.
- Furnace or Heat Pump: The furnace or heat pump is the central component of the HVAC system. It generates heat by burning fuel or extracting heat from the outside air, depending on the system.
- Thermostat: The thermostat is the HVAC system’s control center. It allows users to specify the desired temperature and operates the heating and cooling equipment accordingly.
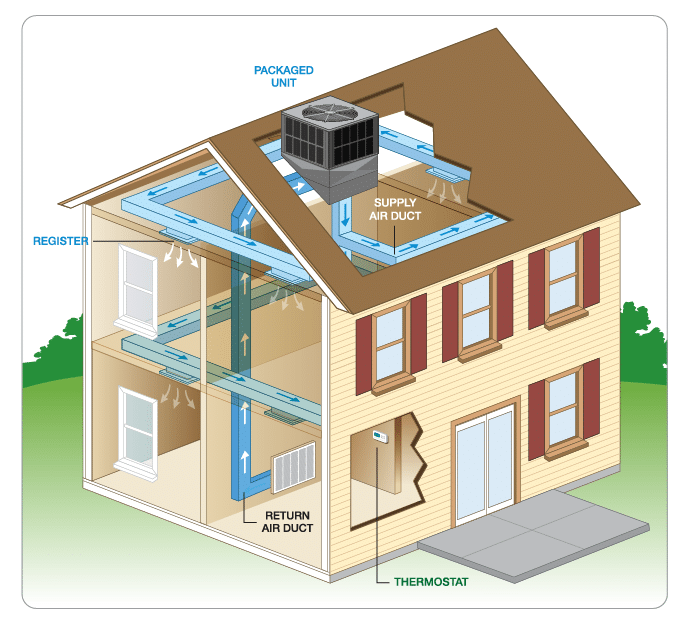
- Ductwork: Ductwork is a system of pipes or tubes that distributes conditioned air throughout a structure. It promotes optimal ventilation and maintains the desired temperature in each room.
These components work together to provide pleasant temperatures while maintaining good indoor air quality.
Recent Advancements
Modern HVAC systems have improved in efficiency, eco-friendliness, and usability as technology has advanced. Some of the most recent developments in HVAC technology include:
- Smart Thermostats: Smart thermostats have transformed how we regulate our HVAC systems. They let users to remotely alter temperature settings, make schedules, and even learn user preferences in order to optimize energy use.
- Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) Systems: VRF systems provide accurate temperature control and zoning capabilities, allowing separate regions of a building to have their own temperature settings. This saves energy and improves comfort.
- High-Efficiency Air Filters: Advanced air filters can remove a variety of airborne contaminants, including dust, allergies, and germs. These filters improve indoor air quality and contribute to a healthier living environment.
- Energy-Efficient Heat Pumps: Modern heat pumps are designed to provide effective heating and cooling. They capture heat from the air or ground using innovative technology, resulting in lower energy use and utility expenditures.
These recent developments have changed the way people perceive indoor comfort, making HVAC systems more sustainable and cost-effective.
The Science Behind Heating And Cooling
Modern HVAC systems regulate indoor temperature through the process of heating and cooling. These systems use innovative technology to regulate airflow and provide a comfortable environment in homes and buildings. HVAC systems provide maximum comfort and energy efficiency by effectively controlling temperature and air quality.
Modern HVAC systems are intended to maintain a comfortable indoor environment by regulating temperature, humidity, and air quality. The heating and cooling processes include the transfer of heat energy from one location to another, which follows thermodynamic principles. Understanding the physics of heating and cooling is critical for designing, implementing, and maintaining energy-saving and cost-effective HVAC systems.
Heat Transfer Principles
Heat energy is transferred by three primary mechanisms: conduction, convection, and radiation. These mechanisms are employed in HVAC systems to move heat from a building’s interior to its exterior, or vice versa. Conduction refers to the transfer of heat through a solid substance, such as a building’s walls or roof. Convection is the process by which heat is transferred through a fluid, such as air or water, after it comes into contact with a heat source or sink. Radiation is the transport of heat via electromagnetic waves, such as infrared radiation, which may penetrate air and other materials.
Thermodynamics In Hvac
Thermodynamics is the discipline of physics that studies the interactions between heat, energy, and work. Thermodynamic principles are employed in HVAC systems to manage interior air temperature and humidity by changing the air’s properties such as pressure, temperature, and moisture content. For example, air conditioning systems utilize a refrigerant to absorb heat from indoor air and release it outside, whereas heating systems use a heat exchanger to transfer heat from a fuel source, such as natural gas or electricity, to indoor air.
Finally, knowing how modern HVAC systems work requires knowledge of the science of heating and cooling. The concepts of heat transmission and thermodynamics are utilized to regulate the temperature and humidity of indoor air, making it more comfortable and healthful for people. By optimizing HVAC systems to be energy-efficient and cost-effective, we can ensure a sustainable future for future generations.
Air Conditioning: A Closer Look
Understanding the operation of air conditioning is critical in modern HVAC systems. Let’s take a closer look at the air conditioning process, which includes the refrigeration cycle and coolants.
Refrigeration Cycle Explained
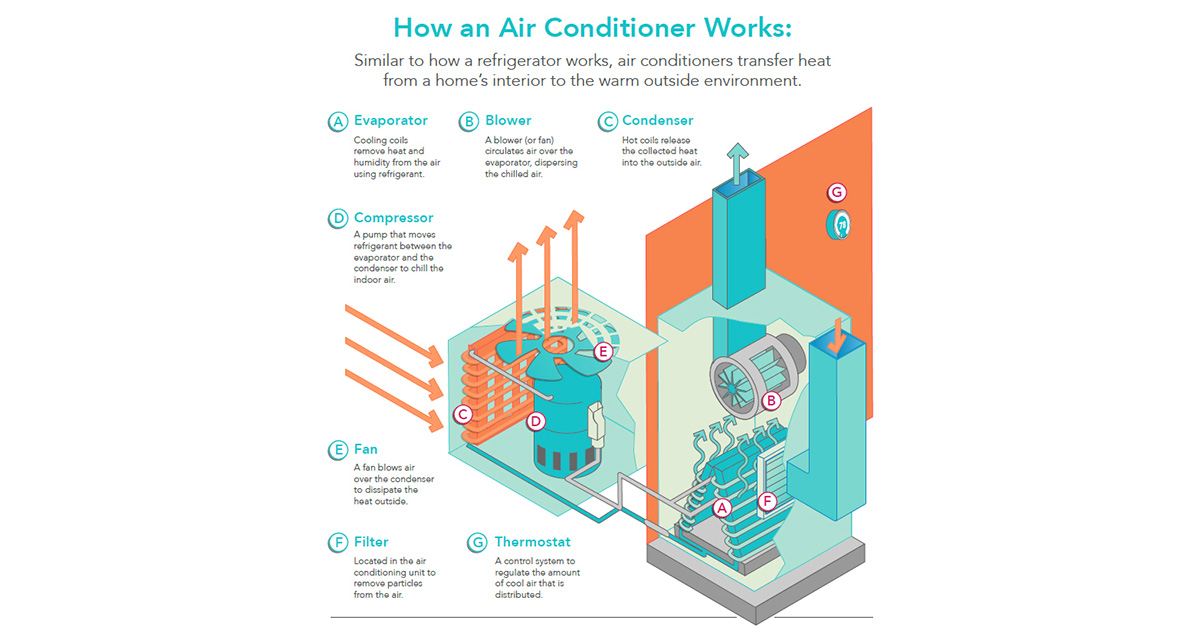
The refrigeration cycle is the primary mechanism for air conditioning. It starts with the compressor, which pressurizes the refrigerant and raises its temperature.
The refrigerant then goes into the condenser, where it loses heat and condenses into a liquid.
The liquid refrigerant then travels through the expansion valve, where it evaporates and absorbs heat from the surrounding air.
Finally, the refrigerant returns to the compressor, restarting the cycle.
Role Of Coolants
Coolants such as R-410A and R-134a are critical components of the air conditioning system. These compounds have large heat capacities and can readily transition from liquid to gas and back again.
By absorbing and releasing heat as they change states, coolants allow the refrigeration cycle to effectively remove heat from inside air and expel it outside, resulting in a cooler indoor environment.
Credit: facthvac.com
Heating Systems Unveiled
Modern HVAC systems are essential for keeping our homes warm and comfortable. Understanding how these systems work allows us to make more educated decisions about how to heat our houses efficiently. In this section, we’ll look at the two major types of heating systems: furnaces and heat pumps, as well as the concept of radiant heating efficiency.
Furnaces
Furnaces are among the most prevalent heating systems used in residential buildings. These trustworthy machines generate heat by burning fuel, such as natural gas or oil. The heat is then dispersed throughout the home via ducts and vents.
Furnaces are classified into two types: gas and oil. Gas furnaces are popular for their efficiency and affordability. They use natural gas as a fuel source, which burns cleanly and circulates warm air around the house.
In contrast, oil furnaces generate heat by burning oil. While they may require a bigger initial investment and more frequent oil supplies, they are a viable choice in locations where natural gas is scarce.
Heat Pumps
Heat pumps provide a more energy-efficient alternative to standard furnaces. These systems operate by transporting heat from one location to another rather than producing heat themselves. They can heat and cool a home, making them adaptable and cost-effective.
There are two types of heat pumps: air-source and geothermal. Air-source heat pumps draw heat from the outside air and transfer it inside. In contrast, geothermal heat pumps use the steady temperature of the ground or a local water supply to heat or cool the property.
Heat pumps are noted for their great efficiency, which can result in significant energy savings. They use a refrigeration cycle to take heat from the air or ground and distribute it throughout the home via ducts and vents.
Radiant Heating Efficiency
Radiant heating systems provide another efficient way to keep houses warm. These systems distribute heat via the floors, walls, or ceilings, resulting in a steady and comfortable temperature across the space.
One of the primary benefits of radiant heating is its efficiency. Unlike forced-air systems, which can cause heat loss through ducts, radiant heating systems direct heat to objects and people in the room, resulting in less wasted energy.
Radiant heating also avoids the circulation of pollen and dust that forced-air systems can cause, making it a healthier alternative for individuals with respiratory concerns. It also ensures more uniform heat distribution, reducing hot and cold patches around the house.
Overall, understanding the many types of heating systems available, such as furnaces and heat pumps, as well as the advantages of radiant heating efficiency, can assist homeowners in making informed choices about their HVAC systems. They can enjoy a comfortable and energy-efficient home all year by selecting the appropriate system.
Ventilation: The Breath Of Fresh Air
Modern HVAC systems control temperature, humidity, and air quality through ventilation. These systems use ducts and fans to bring in fresh air and exhaust stale air, resulting in a comfortable indoor environment. The HVAC system also filters the air to remove impurities, so that people can breathe pure air.
Indoor Air Quality
In today’s modern society, many people and businesses prioritize having clean and fresh indoor air. Poor indoor air quality can cause a variety of health issues and discomfort, hence ventilation systems are an important component of HVAC systems.
Energy Recovery Ventilators
Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERVs) are commonly used in HVAC systems to improve indoor air quality while reducing energy loss. These ingenious gadgets allow for the interchange of stale interior air with fresh outdoor air, all while recovering energy from the departing air.
ERVs use a heat exchanger to transfer heat and moisture between departing and incoming air streams. This procedure promotes a comfortable and steady home temperature while decreasing the need for excessive heating or cooling.
Benefits Of Energy Recovery Ventilators
Energy Recovery Ventilators have numerous benefits for both residential and business areas. This includes:
- Improved Indoor Air Quality: ERVs help to eliminate pollutants, allergens, and odors from indoor spaces, resulting in a healthier and more enjoyable environment.
- Energy Efficiency: By recovering and transmitting energy, ERVs reduce HVAC systems’ overall energy consumption, resulting in cheaper electricity bills.
- Enhanced Comfort: ERVs, which can manage temperature and humidity levels, help to create a more comfortable indoor atmosphere.
- Noise Reduction: ERVs are meant to operate silently, causing little disruption to daily activities and fostering a serene environment.
Finally, appropriate ventilation is essential for ensuring a steady supply of fresh air inside. Energy Recovery Ventilators serve an important role in improving indoor air quality, increasing energy efficiency, and creating a comfortable and healthy living or working space. Individuals and organizations can benefit from clean and fresh air while lowering their environmental impact and energy expenses by incorporating these modern technologies into HVAC setups.
Credit: www.carrier.com
Smart Thermostats And Automation
Smart thermostats and automation have transformed how we manage indoor climate, making HVAC systems more efficient and user-friendly.
Intelligent Temperature Control
Smart thermostats provide accurate temperature management, allowing users to program exact temperatures for different times of day.
This degree of control guarantees that the HVAC system performs at peak efficiency, offering comfort while reducing energy usage.
Energy Savings With Smart Devices
Smart thermostats may learn users’ habits and modify settings automatically, resulting in significant energy savings.
Smart thermostats can optimize energy usage based on user presence in the home by leveraging technologies such as geofencing and occupancy sensors.
Green Hvac Technologies
Modern HVAC systems incorporate Green HVAC Technologies to enhance energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
Solar Powered Systems
Solar panels harness sunlight to power HVAC systems, reducing electricity consumption.
Geothermal Heat Exchange
Geothermal heat exchange systems use the earth’s stable temperature to heat and cool buildings efficiently.
Maintaining An Hvac System
Maintaining an HVAC system is crucial for optimal performance and longevity.
Regular Maintenance Tips
- Change air filters every 1-3 months.
- Keep outdoor unit free of debris.
- Schedule professional inspections annually.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- If system is not cooling, check thermostat settings.
- Strange noises may indicate belt or motor issues.
- Foul odors can signal mold or electrical problems.
Future Of Hvac: Innovations On The Horizon
HVAC systems are continually developing, with exciting advancements affecting the future of indoor comfort. The combination of innovative technologies and sustainable practices is propelling the HVAC sector forward in a more efficient and environmentally responsible direction.
Emerging Trends
Smart thermostats optimize temperature control to save energy.
IoT connectivity enables remote monitoring and control of HVAC systems.
Air quality monitors improve indoor air filtering and purification.
Sustainability And Efficiency
HVAC units that are energy efficient have a lower carbon footprint and lower operating costs.
Green refrigerants encourage eco-friendly cooling solutions.
Solar-powered HVAC systems use renewable energy to operate sustainably.

Credit: www.mitsubishicomfort.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does An HVAC System Work?
An HVAC system circulates air through ducts and vents. The system heats or cools the air as needed and filters out contaminants before returning it to the home or building.
What Are The Components Of An Hvac System?
An HVAC system typically consists of a furnace, an air conditioner, a thermostat, ducting, and vents. The furnace heats the air, while the air conditioner cools it. The thermostat regulates the temperature, while the ductwork and vents move air throughout the building.
What Is The Purpose Of An Air Filter In An Hvac System?
An HVAC system’s air filter removes contaminants like dust, pollen, and pet dander from the air before it is pumped back into the building. This improves air quality and may also assist to extend the life of the HVAC system.
How Often Should I Change The Air Filter In My Hvac System?
Air filters in HVAC systems should be changed every 1-3 months, depending on consumption and filter type. A filthy filter can impede airflow and impair the system’s efficiency, therefore regular maintenance is required.
Conclusion for How Do Modern HVAC Systems Work
Modern HVAC systems operate by efficiently managing indoor temperature and air quality. These systems improve energy efficiency and comfort by using innovative technologies like smart thermostats and variable-speed motors. Understanding how these systems work might help homeowners make more informed HVAC selections.

