Affiliate Disclosure
HVAC Guide Guys is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.
How HVAC Cooling Works? Ever wondered how your home turns cool and comfy in minutes? Learning about HVAC cooling can make this magic clear. It’s the tech that keeps you cool when it’s hot outside.
Air conditioning is more than just cold air. It’s a complex process that removes heat from your home. This makes your space cooler by moving warmth outside.
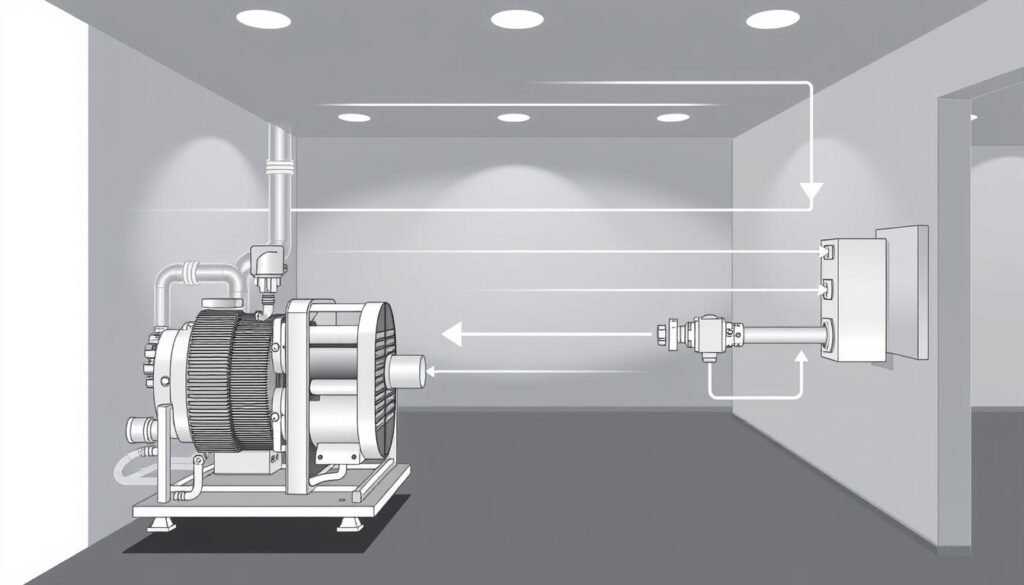
Most homes in North America have split-system air conditioners. These systems have many parts working together. They move refrigerant between indoor and outdoor units to cool your home.
The cooling process involves six main parts: a thermostat, outdoor unit, indoor unit, copper tubing, expansion valve, and ductwork. Each part is important for keeping your home at the right temperature.
Key Takeaways
- Air conditioning removes heat and humidity from indoor spaces
- Split-system ACs are the most prevalent cooling technology
- Refrigerant is the primary mechanism for heat transfer
- HVAC systems involve complex heat exchange processes
- Proper maintenance ensures optimal cooling performance
Table of Contents
The Basic Principles of HVAC Cooling Systems
Learning how your home stays cool is fascinating. With about 87% of US homes using air conditioning, it’s key to know how it works. This knowledge helps keep your home comfortable.
The cooling process in HVAC systems is based on important scientific ideas. These ideas work together to control your home’s temperature. The system moves heat from inside your home to the outside, making it cool.
Understanding Heat Transfer
Heat transfer is essential for air conditioning. Your AC moves heat from one place to another. It uses three main ways:
- Conduction: Direct heat transfer through physical contact
- Convection: Heat movement through fluid or air circulation
- Radiation: Heat transfer through electromagnetic waves
The Role of Refrigerant
The ac compressor is key in refrigerant’s role. This special chemical helps your cooling system work well. It changes from liquid to gas and back again, moving heat.
“Refrigerant is the unsung hero of your cooling system, silently managing temperature with remarkable precision.”
Temperature Control Fundamentals
Modern HVAC systems keep your home at the right temperature. They use smart thermostats that save energy. These thermostats can cut energy use by 10-15% by following your schedule.
Knowing these basics helps you see the science behind cooling your home. It makes your home cool and comfortable.
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopCore Components of Your AC System
Your air conditioning system is made up of many parts working together. These parts keep your home cool and comfortable. Knowing about these parts helps you understand how your AC works.
The evaporator coil is key in cooling your home. It’s inside your indoor unit and pulls heat from the air. This makes your home feel cooler. Refrigerant flows through it, changing from liquid to gas as it absorbs heat.
- Indoor Unit: Contains the evaporator coil and blower fan
- Outdoor Unit: Houses the condenser coil and compressor
- Copper Tubing: Connects different system components
- Expansion Valve: Regulates refrigerant flow
- Ductwork: Distributes cooled air throughout your home
The condenser coil is also vital. It’s outside and releases the heat from your home into the air. This lets the refrigerant cool down and turn back into a liquid. It’s ready for another cooling cycle.
“A well-maintained AC system is the key to year-round comfort and energy efficiency.” – HVAC Experts
Modern HVAC systems are built with care. The compressor is the system’s heart, moving refrigerant between coils. The blower fan moves air, and the expansion valve controls refrigerant pressure and temperature.
Keeping these parts in good shape helps your system last longer. Regular checks by pros can spot problems early, saving you money on big repairs.
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopHow HVAC Cooling Works: The Complete Process
Learning about your home’s cooling system is fascinating. It shows how heat is moved and temperatures are controlled. The hvac refrigeration cycle makes your home cool and comfortable through several steps.
Modern air conditioning systems use a complex but effective process. They have many parts working together. The cooling starts when the thermostat notices temperature changes and starts the refrigerant flow.
The Cooling Cycle Explained
The cooling cycle has several important steps. It turns warm indoor air into cool air:
- Warm air is pulled into the system through return air vents
- Refrigerant takes heat from indoor air
- Compressed refrigerant moves heat outside
- Cooled air is spread throughout your home
Refrigerant Flow and Heat Exchange
Refrigerant is key in the heat exchange process. As it moves through copper tubes, it changes from liquid to gas. This process absorbs and releases heat well.
| Component | Function | Temperature Change |
|---|---|---|
| Evaporator Coil | Absorbs Indoor Heat | Cools Air |
| Compressor | Pressurizes Refrigerant | Increases Temperature |
| Condenser Coil | Releases Heat Outdoors | Reduces Refrigerant Temperature |
Air Distribution Methods
Forced-air systems use electric blowers to spread cooled air. These systems can use up to 30% of your home’s energy. So, it’s important to design them efficiently to keep your home cool and save energy.
“The magic of air conditioning lies not just in cooling, but in strategic heat management.” – HVAC Engineering Insights
Inside Your Indoor AC Unit
Your indoor AC unit is key to keeping your home cool. It has two main parts: the evaporator coil and the AC fan. These work together to make your living space comfortable.
The evaporator coil is vital for cooling. Warm air from your home hits this coil and loses heat. This makes the air cooler, turning it into a refreshing breeze.
- Evaporator coil role: Absorbs indoor heat
- AC fan operation: Circulates cooled air throughout your home
- Primary function: Temperature regulation
The AC fan is also important for keeping temperatures right. It blows air over the evaporator coil, spreading cool air through your home. This keeps every room at a comfortable temperature.
“The magic of air conditioning happens inside this compact unit, where heat transfer and air movement work in perfect harmony.”
It’s important to take care of your indoor AC unit. Clean the evaporator coil and make sure air can flow freely. This helps your system work well, possibly making it last 10-15 years longer.
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopThe Outdoor Unit: Functions and Features
Your air conditioning system’s outdoor unit is key to cooling your home. It works hard to remove heat and keep your indoor temperatures comfy.
The outdoor unit has three main parts that work together. These parts are vital for cooling your home. Knowing about them helps you understand your AC system better.
Compressor Operation: The Heart of Cooling
The compressor is at the heart of cooling. It’s like a pump, moving refrigerant and raising its pressure. This makes the refrigerant hot and high-pressure, ready to take away heat.
- Increases refrigerant pressure
- Moves refrigerant through the system
- Enables heat transfer mechanism
Condenser Coil Mechanics
The condenser coil’s job is to get rid of heat from inside your home. Made from copper or aluminum, these coils are great at transferring heat. A big fan blows outdoor air through the coils, making sure heat is released well.
| Coil Material | Thermal Conductivity | Heat Transfer Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Copper | 390 W/(m·K) | Excellent |
| Aluminum | 205 W/(m·K) | Very Good |
Heat Dispersion Process
The outdoor unit’s fan is key for spreading out heat. It helps get rid of heat from inside, keeping your home cool. About 70% of homes use this air-cooled method.
“A well-maintained outdoor unit can improve system efficiency by up to 20%” – HVAC Maintenance Experts
It’s important to keep your outdoor unit clean. Clearing away debris helps it work better and last longer.
Understanding the Refrigeration Cycle
The hvac refrigeration cycle is the secret behind your home’s cooling. It turns warm air into cool air through a dance of thermodynamics and refrigerant flow. This process is amazing.
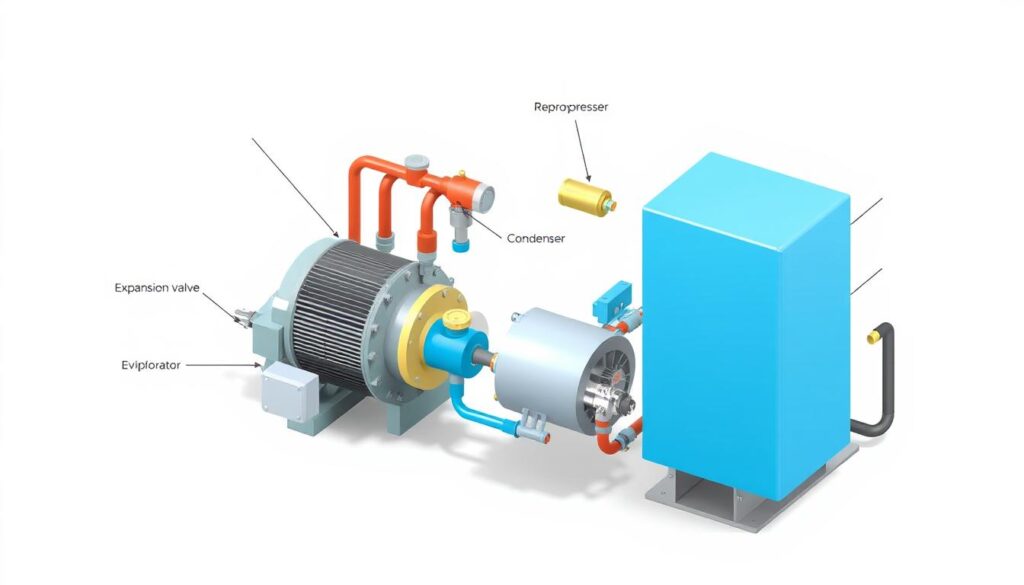
- Compressor: The system’s mechanical heart
- Condenser: Where heat is released
- Metering Device: Controls refrigerant flow
- Evaporator: Absorbs indoor heat
Refrigerant is very important in this process. It changes from liquid to gas, taking in and giving out heat efficiently. As it moves, the refrigerant goes through big changes:
- It starts as a cool vapor in the compressor
- Then, it gets compressed into a hot gas
- Next, it goes to the condenser to lose heat outside
- It turns into a high-pressure liquid
- Then, it expands and cools in the metering device
- Lastly, it absorbs indoor heat in the evaporator
“The refrigeration cycle is nature’s own cooling miracle, turning warmth into comfort with scientific precision.” – HVAC Engineering Insights
Today’s systems use cool refrigerants like R32 and R410A. These are made to cool efficiently and protect the environment. Knowing about this cycle helps you understand how your AC keeps your home cool.
The Role of Thermostats in HVAC Operation
Your thermostat is the brain of your home’s air conditioning system. It controls how cooling works with precision and intelligence. Modern thermostats do more than just turn your AC on and off. They are smart devices that manage your home’s comfort and energy use.
Understanding air conditioning starts with knowing your thermostat’s role. These smart devices keep your home’s temperature just right. They work with your HVAC system to make sure you’re comfortable.
Temperature Monitoring
Thermostats track indoor temperatures very accurately. Studies show a well-placed thermostat can make your HVAC system 20% more efficient. The right spot ensures accurate readings and cuts down on system cycling.
System Communication
- Sends signals to activate cooling when temperature rises
- Communicates with indoor and outdoor HVAC units
- Manages system components for optimal performance
Programming Options
Modern thermostats offer great flexibility in managing your home’s climate. Programmable and smart thermostats can cut energy costs a lot:
| Thermostat Type | Energy Savings | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Programmable Thermostats | 10-30% | Scheduled temperature adjustments |
| Smart Thermostats | 15% average reduction | Learning capabilities, remote control |
Roughly 50% of American households now use digital thermostats, reflecting a growing trend towards smarter home climate management.
By using your thermostat’s full range of features, you can make your HVAC system work better. This means less energy use and more consistent comfort at home.
Air Distribution and Ductwork Systems
Your home’s HVAC system uses a network of air ducts to keep temperatures right. The ac fan is key in moving cooled air from the central unit to your rooms.
Ductwork is like your home’s temperature control circulatory system. It carries conditioned air using smart engineering. This makes your home comfortable and efficient.
“Proper air distribution is the key to maintaining consistent temperatures and optimal comfort in your home.”
Key Components of Air Distribution
- Supply vents that release cooled air into rooms
- Return air grilles that collect air for recirculation
- Flexible and rigid ductwork materials
- Air pressure management systems
Different duct systems fit different homes:
- Radial systems
- Extended plenum configurations
- Reducing trunk designs
- Perimeter loop layouts
High-efficiency systems with variable-speed fans can optimize airflow while minimizing energy consumption. Experts say clean your ducts every five years. This keeps your HVAC system running well.
Knowing about your home’s air system shows how complex comfort is.
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopEnergy Efficiency in Modern AC Systems
Modern HVAC systems have changed how we cool our homes. They focus on saving energy without losing comfort. Today’s air conditioning technologies are amazing at cutting down energy use while keeping us cool.

Energy-efficient AC systems are a big step forward in cooling technology. They use less electricity without losing performance.
SEER Ratings Explained
The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) shows how efficient an AC is. SEER ratings let you compare different AC units’ energy use:
- Higher SEER ratings mean more efficient cooling
- Modern units can have ratings up to 26
- ENERGY STAR certified units are about 15% more efficient
Energy-Saving Features
Modern HVAC systems use new technologies to save energy:
- Variable-speed compressors adjust cooling as needed
- Smart thermostats control temperature better
- Multi-speed blower fans use less energy
“Investing in an energy-efficient AC system is not just about saving money, but also reducing environmental impact.”
| Efficiency Feature | Energy Savings |
|---|---|
| Variable Capacity Systems | Up to 30% more efficient |
| Smart Thermostat Control | 15-20% less cooling costs |
| Proper System Maintenance | Up to 20% better performance |
Choosing an energy-efficient AC system can lower your monthly bills and help the environment.
Common Types of HVAC Cooling Systems
Knowing about different HVAC cooling systems helps you choose the best for your home. Each system has its own way of cooling, fitting different homes.
- Split-System Air Conditioners: The most common choice for homes
- Packaged Air Conditioners: Great for small spaces
- Ductless Mini-Split Systems: Perfect for cooling specific areas
Let’s dive into these cooling systems:
| System Type | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Split-System | Indoor and outdoor units, traditional ductwork | Standard homes with existing ductwork |
| Packaged AC | Compact single-unit design, roof or ground installation | Small homes, apartments, limited space |
| Ductless Mini-Split | No ductwork, zone-based cooling | Homes without ducts, room additions |
“Choosing the right HVAC system is about matching your home’s unique cooling needs with the most efficient technology.” – HVAC Expert
When picking a system, think about your home’s size, current setup, and energy goals. Each system has its own benefits, helping you find the best match for your comfort and budget.
Maintaining Optimal System Performance
Keeping your HVAC system in top shape needs regular care. The cooling process relies on maintenance for the best performance and energy use. Taking care of your system early can save you money and prevent big repairs.
Knowing how hvac cooling works shows why maintenance is key. If you ignore your system, it might not work as well and could break down unexpectedly.
Essential Maintenance Tasks
- Replace air filters every 1-3 months
- Clean outdoor condenser coils regularly
- Clear debris around outdoor units
- Check refrigerant levels
- Inspect electrical components
Performance Optimization Strategies
| Maintenance Action | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regular filter changes | Improve airflow efficiency by up to 15% |
| Annual professional inspection | Reduce unexpected breakdowns by 50% |
| Cleaning condenser coils | Enhance system efficiency by 10-30% |
| Sealing ductwork | Improve system efficiency by 20-30% |
“Preventative maintenance is the key to a long-lasting and efficient HVAC system.”
By following these maintenance tips, you could save $300 to $600 a year on energy. Plus, your cooling system will work at its best.
Conclusion
Learning about HVAC cooling can really change how comfortable your home is. It also helps save energy. Knowing how air conditioning works lets you keep your home cozy and use less power.
Your HVAC system does more than cool the air. It can last 15 to 20 years with the right care. Keeping it in good shape can even make your home more valuable by 10-15%.
Modern cooling tech is amazing at saving energy. Smart thermostats and high-efficiency filters can cut your bills by up to 15%. Knowing how HVAC cooling works helps you make smart choices about your system.
Spending time learning about your cooling system is worth it. It leads to better comfort, lower bills, and less harm to the environment. Whether you’re new to homeownership or want to improve your current system, knowing is key.

