Affiliate Disclosure
HVAC Guide Guys is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.
Does Japan Have HVAC? As the sun shines brightly on Tokyo’s busy streets, we all appreciate the comfort of modern cooling systems in Japan. I remember my grandparents using paper fans and open windows to cool down. But now, Japan has adopted HVAC technology, changing how people control their indoor climate.

Key Takeaways
- Japan widely uses HVAC systems, with 72% of housing units equipped with heat pump air-conditioning systems as of 1990.
- Japanese residential heat pumps commonly combine cooling, dehumidifying, and heating in a single system, focusing on cooling persons rather than spaces.
- These systems are typically ductless-split type with exterior compressors and interior heat exchanger units, designed for compact urban living.
- The Japan HVAC Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Equipment Market size reached a valuation of USD xx.x Billion in 2023 with projections to achieve USD xx.x Billion by 2031.
- The Asia-Pacific region, including Japan, is experiencing rapid growth in the HVAC Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Equipment Market.
Table of Contents
Understanding Japanese HVAC Evolution and History
Japan’s heating and cooling systems have changed a lot over the years. This change shows the country’s growth in technology and its changing cities. From old ways to new HVAC systems, Japan’s story is interesting. It shows how the nation has improved in engineering and adapting to the environment.
Traditional Heating Methods in Japan
In the past, the Japanese used smart ways to warm themselves, not the whole room. The hibachi, a portable charcoal brazier, and the kotatsu, a low table with a heating element, were common. These methods were good for the climate and saved energy, which is important today.
Transition to Modern Cooling Systems
In the 1950s and 1960s, Japan started using more common heaters like kerosene or gas room heaters and electric kotatsu. The 1980s brought heat pump systems, changing how homes and buildings were cooled and heated. This change made HVAC systems more efficient and flexible.
Impact of Urban Development
As Japan’s cities grew, the need for better HVAC systems grew too. Modern homes and buildings were built tighter, making cooling and heating harder. This led to the creation of new HVAC technologies, designed to meet the challenges of Japan’s cities.
“The story of Japanese heating and cooling systems offers a fascinating glimpse into the nation’s engineering prowess and environmental adaptability.”
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1881 | Willis Carrier’s slide rule, a circular calculating instrument, was patented, assisting in the calculation of dew point control, a foundational aspect of modern air conditioning. |
| 1902 | The world’s first modern air conditioning system was installed at a printing plant in Brooklyn, New York. |
| 1937 | Carrier established close ties with Japan, supplying air conditioning equipment to the Fuji Silk Spinning Company of Yokohama in 1907. |
| 1950 | Willis Carrier, known as the “Father of Air Conditioning,” passed away at the age of 74 in New York City. |
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopDoes Japan Have HVAC: A Comprehensive Overview
Japan’s Japanese HVAC market is strong, with lots of air conditioning around. By 1990, 72% of homes had heat pump air-conditioning systems. This shows how key heating and cooling systems are there.
Japanese HVAC systems do more than just cool or heat. They also remove moisture. People like these all-in-one systems because they meet many needs. This is especially true in Japan’s varied climate and lifestyle.
- The Japan HVAC market is expected to grow by USD 2.7 Billion from 2024 to 2029. This growth is due to energy-saving tech and better indoor air.
- Daikin Industries is a leader in green HVAC solutions. They use R-32 refrigerant, which is better for the planet.
- Panasonic Corporation has a wide range of HVAC products. They include air purifiers and smart devices that connect to the internet.
- Air Water Inc. is making waves with its use of air and water for heat pumps. This is a new approach in the industry.
The Japanese HVAC market focuses on different types of equipment. There’s a big push for air conditioning, ventilation, and energy-saving heating. This variety meets the needs of homes, businesses, and factories across Japan.
“Japan’s commitment to innovation, collaboration, and continuous improvement in the HVAC industry is driving the development of next-generation solutions aligned with energy efficiency and carbon neutrality goals.”
The Japan HVAC market keeps growing. It shows Japan’s effort to make homes more comfortable, save energy, and protect the environment. They use the latest HVAC tech and solutions for a better future.
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopJapanese HVAC Market Leaders and Manufacturers
Japan is a hub for top HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) makers. They are known for their cutting-edge tech and leading market share. These brands are always pushing the limits of what’s possible in HVAC.
Major Companies and Brands
Daikin Industries, Mitsubishi Electric, Panasonic, Fujitsu, and Toshiba are the big names in Japan’s HVAC scene. They’re famous for their quality, tech, and strong brand presence worldwide.
Technology Innovation Leaders
Japanese HVAC makers are leading the tech charge. They’re introducing new stuff like inverter tech, smart controls, and energy-saving features. These innovations make them top choices for eco-friendly and high-performance HVAC solutions.
Market Share Distribution
The Japanese HVAC market is split among many players, but a few stand out. Daikin and Mitsubishi lead with a big chunk of the market. They keep investing in R&D to stay ahead and meet market demands.
As Japan’s HVAC market grows, thanks to urbanization and green efforts, these brands are set to lead the way. They’re shaping the future of HVAC in Japan and around the world.
Modern HVAC Systems in Japanese Homes
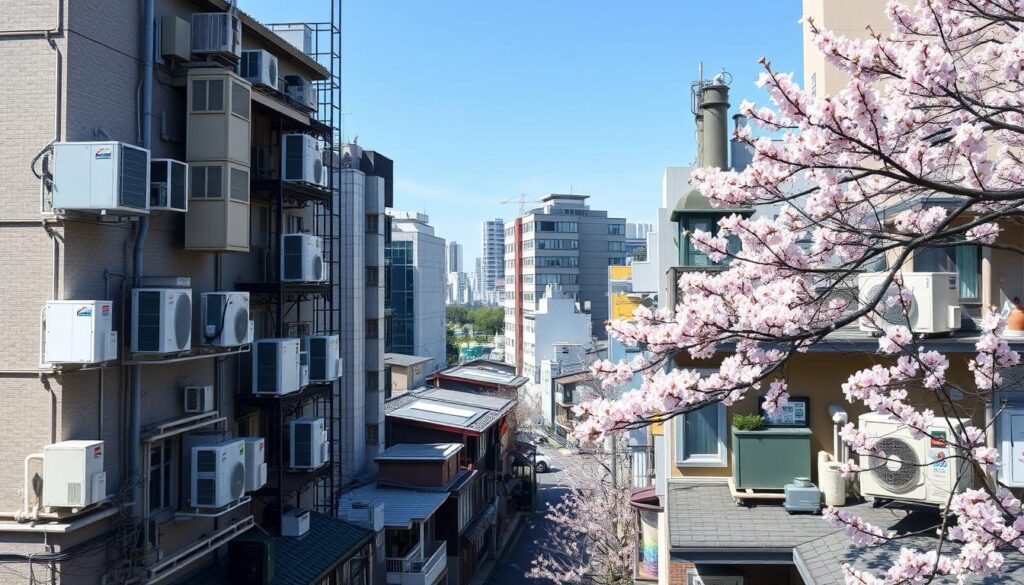
In Japan, the most common HVAC Japan system is the ductless-split type heat pump. These units are small and efficient. They have an exterior compressor and an interior heat exchanger, connected through a small wall opening.
The interior units are wall-mounted near the ceiling. The exterior units are placed discreetly on roofs or outside walls.
These modern air conditioning systems are popular in Japan. They offer personalized climate control for individual rooms. This meets the Japanese preference for customized comfort.
These systems cool or heat specific areas. Unlike traditional central HVAC systems, they serve individual rooms, not the whole home.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Compact Design | Ductless-split systems have a small footprint, allowing for flexible installation options in Japanese homes with limited space. |
| Energy Efficiency | These systems are engineered to optimize energy consumption, contributing to lower utility bills and a more sustainable home environment. |
| Personalized Comfort | The ability to control the temperature and airflow in individual rooms caters to the Japanese preference for personalized comfort. |
Ductless-split heat pump systems are the top choice for modern Japanese homes. They offer a mix of functionality, energy-efficiency, and personalized comfort.
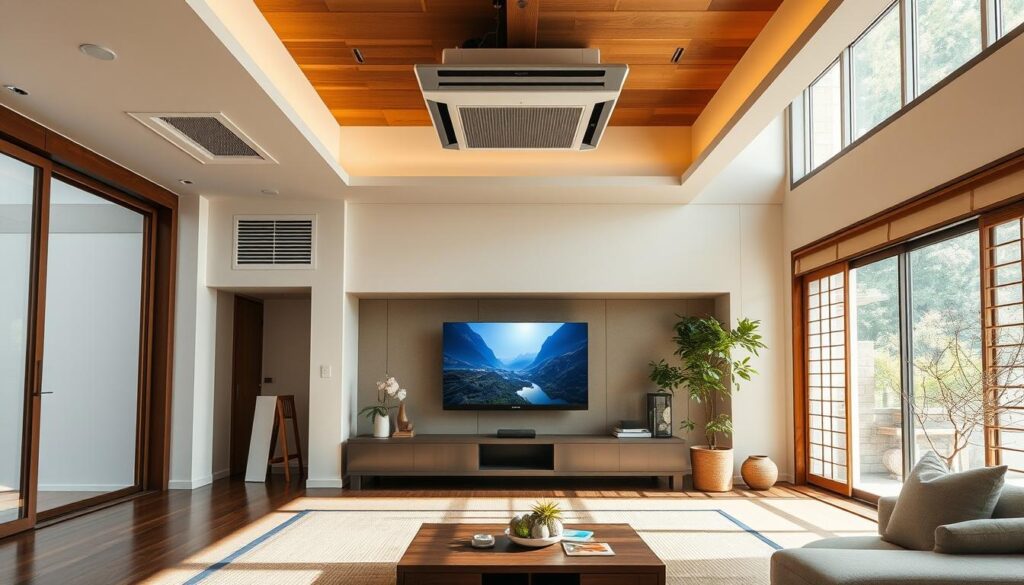

Unique Features of Japanese Air Conditioning Technology
Japan’s HVAC industry leads with innovative tech that focuses on saving energy and personal comfort. These advancements make Japanese air conditioning stand out from systems in many Western countries.
Inverter Technology
Inverter technology is key in modern Japanese air conditioning units. Unlike old compressors, inverter-driven ones adjust their speed to meet cooling or heating needs. This precise control cuts down energy use and keeps the indoor space stable and comfy.
Smart Control Systems
Japanese air conditioning systems have advanced control systems that learn from you. These “smart” systems adjust temperature, humidity, and airflow based on your habits. Some even create natural-like wind and temperature changes for a better feel.
Energy Efficiency Features
Energy saving is big in Japan, and it shows in their HVAC tech. Japanese air conditioners have strong insulation, efficient compressors, and top-notch filters to save energy. They also have special modes like dehumidification and automatic operation to save even more.
These special features show Japan’s dedication to offering comfy, energy-saving, and cutting-edge HVAC solutions.
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopResidential HVAC Installation Trends
In Japan, the demand for efficient HVAC systems is growing. Homeowners are now looking for heat pump systems. These systems can heat and cool homes all year round.
Unlike in Western countries, most Japanese homes don’t come with built-in HVAC systems. Instead, homeowners choose to install their own. This choice has made combination heating and cooling units very popular. They adapt well to Japan’s changing weather.
| Key Drivers of Japan’s Residential HVAC Installation Trends | Market Share of Major Players |
|---|---|
|
|
The Japan Residential Unitary HVAC market is expected to grow. It will go from $24.83 billion in 2023 to $35.8 billion by 2032. This growth is due to the need for energy-efficient and advanced HVAC installation Japan. It’s also because of the increasing demand for residential cooling trends and Japanese home heating solutions.

“The integration of smart home technologies and the emphasis on energy efficiency have become key factors driving the residential HVAC market in Japan.”
Commercial and Industrial HVAC Applications
In Japan, the commercial and industrial sectors use advanced HVAC systems. Companies like Mitsubishi Electric and Daikin provide solutions for big buildings. They focus on saving energy and improving performance.
Office Building Solutions
The Japan commercial HVAC market is set to hit USD 4.56 billion by 2029. It will grow at 7.16% annually from 2024 to 2029. This is because of the need for energy-saving HVAC in offices and malls.
New technologies, like inverter systems and smart controls, help these HVAC systems. They keep the indoor climate perfect while using less energy.
Industrial Facility Systems
In the industrial world, commercial HVAC Japan and industrial cooling systems are key. They keep the environment right for making things and keeping products quality. These office air conditioning systems meet the special needs of factories, ensuring the right temperature and air quality.
Japan is getting more into saving energy and being green. This push for sustainability is making advanced HVAC systems more popular. As Japan aims for zero-energy buildings by 2030 and 2050, the need for green HVAC will grow. This opens up chances for companies to grow and bring in new tech.
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopEnvironmental Impact and Energy Efficiency
In Japan, HVAC Japan systems focus on saving energy and reducing environmental impact. They use new energy-efficient cooling tech, like smart compressors and control systems. The goal is to make air conditioning more sustainable by using renewable energy.
The global market for energy-saving air conditioners was worth $XX billion in 2020. It’s expected to hit $XX billion by 2025, with Asia leading the way. This growth is thanks to demand for eco-friendly air conditioners and coolers that use water evaporation.
| Key Players in the Energy-Efficient HVAC Market | Market Share by Region |
|---|---|
|
|
In Japan, air conditioner use has grown a lot in homes over the last 30 years. This is thanks to better energy-saving tech. Now, homes use less energy for cooling thanks to new air conditioners and heat pumps.
“In traditional Japanese households, out of 16 families studied, 14 had at least one air conditioner, and the duration of their usage increased significantly, particularly initiated by male adults in the household.”
The Japanese government has helped by making energy-saving laws since 1979. Now, buildings must use energy-saving features. This makes buildings more eco-friendly and saves money on energy costs.
Japan is a leader in eco-friendly HVAC Japan and energy-efficient cooling tech. Their focus on sustainable air conditioning is changing the HVAC industry worldwide.
Future Developments in Japanese HVAC Technology
Japan’s HVAC technology is set to see big changes. Two main areas will lead the way: smart home tech and green solutions. The market is expected to grow fast, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) from 2024 to 2032.
Smart Home Integration
Smart home tech is changing how Japanese homes stay cool and warm. New HVAC systems work with IoT devices and AI for better control. This means homeowners can adjust their comfort with just a few taps or voice commands.
These systems also help save energy. They make homes more comfortable and efficient, improving life for everyone.
Sustainable Solutions
Sustainability is a big deal in Japan’s HVAC world. Companies are working on greener refrigerants and systems that use solar power. This move aims to cut down on carbon emissions and help the planet.
They also focus on better air quality and comfort. This makes homes healthier and more comfortable for families.
As the market grows, these advancements will be key. They’ll meet the need for energy-saving, custom, and eco-friendly systems.
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopComparing Japanese and Western HVAC Systems
In the world of HVAC, Japan and the West have their own ways. Western systems aim to cool the whole house. In contrast, Japan focuses on cooling each room separately. Japanese units are smaller and do more, like heating and dehumidifying.
Energy efficiency and smart controls are big in Japan. Their HVAC systems use advanced tech like inverter technology. This shows Japan’s commitment to saving energy and being green.
| Feature | Japanese HVAC Systems | Western HVAC Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Approach | Room-by-room climate control | Whole-house cooling |
| Unit Size | Compact, multi-functional | Larger, single-purpose |
| Energy Efficiency | Highly efficient with advanced features | Varying levels of efficiency |
| Smart Controls | Sophisticated, integrated systems | Varying levels of automation |
Western HVAC systems have their own benefits. But Japan’s cooling tech is all about new ideas, saving energy, and making things easy for users. As the HVAC market grows, it’s interesting to see how different cultures approach cooling.
“The Japanese HVAC market is anticipated to continue growing due to upcoming major events like the Tokyo Summer Olympics and a world expo in 2025 in Osaka.”
Conclusion
Japan’s HVAC scene has changed a lot, moving from old heating ways to modern cooling systems. The country leads in air conditioning tech, focusing on saving energy, being small, and doing many things at once. This makes Japan a top player in the field.
We looked at how HVAC in Japan grew, the big names in the business, and what makes Japanese air conditioning special. We also saw how it’s used in homes and businesses. By 1990, over 72% of homes had heat pump air-conditioning systems.
Japan keeps pushing the limits in HVAC, using new tech like inverter systems and smart controls. They also make systems that can heat and cool. This shows Japan’s dedication to making HVAC better, offering lessons for the world.