Affiliate Disclosure
HVAC Guide Guys is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.
Understanding How HVAC Works ? Ever wondered how your home stays comfy, no matter the weather? Your HVAC system is the secret to indoor comfort. It works quietly to keep your living space just right.
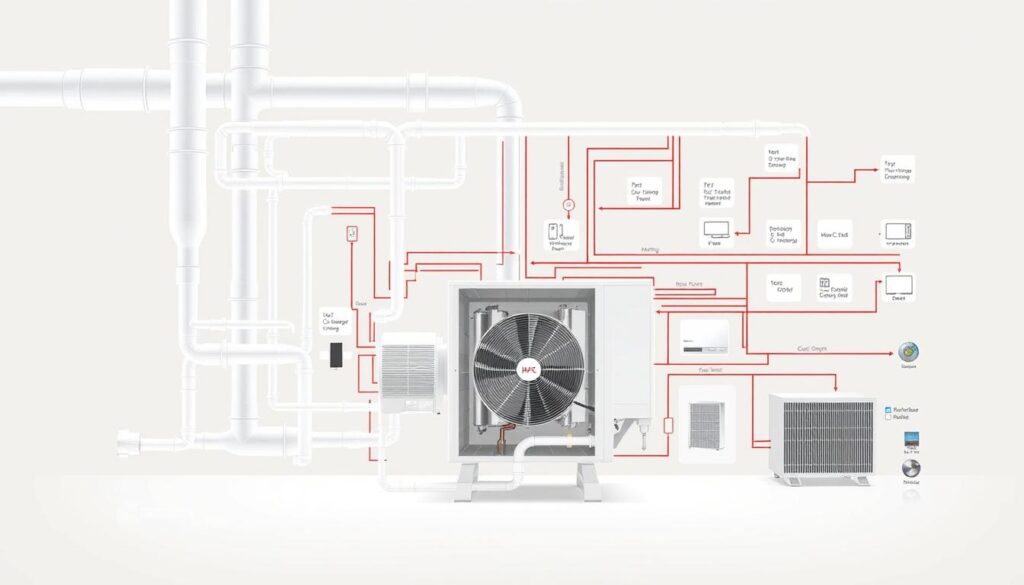
An HVAC system is more than a machine. It’s a complex network of parts that heats, cools, and moves air in your home. The how HVAC works diagram shows how it changes air quality and temperature with great accuracy.
Today’s HVAC parts work together perfectly to make your home climate just right. From the outdoor unit to the indoor air handler, each part is key to keeping your home comfy.
Key Takeaways
- HVAC systems control temperature and air quality in residential spaces
- Approximately 89% of U.S. homes rely on HVAC systems for heating and cooling
- A well-maintained system can improve energy efficiency by 15% to 30%
- HVAC systems account for 40% of total energy use in residential homes
- Proper maintenance can extend system lifespan up to 25 years
Table of Contents
Introduction to HVAC Systems and Their Importance
HVAC systems are the quiet heroes of modern life. They work hard to make our homes and workplaces comfortable. These systems do more than just control the temperature. They change how we live and work.
Understanding HVAC systems is key in residential hvac maintenance. At their heart, they aim to provide comfort by managing temperature and air quality.
What Makes HVAC Systems Essential for Modern Living
Modern life needs comfortable indoor spaces. HVAC systems offer big benefits:
- Consistent temperature control
- Improved air quality
- Humidity regulation
- Enhanced personal comfort
Basic Principles of HVAC Operation
HVAC systems use science to work. They move heat around to make our spaces comfy.
| System Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Compressor | Pressurizes refrigerant |
| Condenser | Releases heat outside |
| Evaporator | Absorbs indoor heat |
Impact on Indoor Comfort and Air Quality
A good HVAC system does more than just control temperature. It also manages humidity and filters out bad air. Keeping these systems in top shape is vital for our comfort and health.
A well-maintained HVAC system is the key to creating a comfortable, healthy indoor environment.
Core Components of a Modern HVAC System
It’s important to know the key parts of an HVAC system to understand how your home stays comfortable. These systems have many parts that work together. They control the temperature and air quality inside your home.
- Outdoor Unit (Condenser)
- Indoor Unit (Evaporator)
- Refrigerant Lines
- Air Handler
- Ductwork
When installing HVAC systems for businesses, it’s vital to think about these parts. Each one is essential for keeping the indoor air just right.
“The efficiency of an HVAC system depends on the seamless interaction of its core components.” – HVAC Engineering Experts
Now, let’s look at what each part does:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Outdoor Unit | Heat Rejection | Releases accumulated heat outside |
| Indoor Unit | Air Cooling/Heating | Processes and circulates conditioned air |
| Refrigerant Lines | Heat Transfer | Carries refrigerant between units |
| Air Handler | Air Circulation | Moves conditioned air through ductwork |
| Ductwork | Air Distribution | Channels air to different rooms |
About 100 million American homes use these advanced HVAC parts to keep the air inside comfy. Regular upkeep keeps these systems running well and lasting longer.
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopHow HVAC Works Diagram: A Detailed Look
Learning about your HVAC system can make you appreciate the tech that keeps your home cozy. A how hvac works diagram shows how heat and air are moved around your home.
HVAC systems are amazing feats of engineering. They control your home’s climate with great accuracy. The system uses a complex cycle of heat transfer and air movement, with key parts working together smoothly.
The Cooling Cycle Explained
The cooling cycle is a key part of how hvac airflow diagram shows refrigerant movement. It has several important steps:
- Refrigerant absorbs indoor heat at the evaporator coil
- Compressed refrigerant moves to the outdoor condensing unit
- Heat is released outside through the condenser coils
- Cooled refrigerant returns to the indoor unit to restart the cycle
The Heating Process Visualization
When it’s time to heat up, HVAC systems turn electrical or combustion energy into warmth. Heat pumps or furnaces make thermal energy, which is spread through ductwork.
| Heating Method | Energy Source | Efficiency Range |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Pump | Electricity | 300-400% |
| Gas Furnace | Natural Gas | 80-98% |
| Electric Furnace | Electricity | 95-100% |
Airflow Patterns and Distribution
Good airflow is key for steady indoor temperatures. The hvac airflow diagram shows how conditioned air moves through ducts. This ensures even heating in all rooms.
“Efficient airflow is the heart of effective temperature management.” – HVAC Engineering Experts
Your HVAC system always checks and tweaks air flow. It makes a comfy space just for you.
Understanding the Outdoor Unit Components
Your HVAC system’s outdoor unit is key to keeping your home comfy. Almost 100 million people in the U.S. count on these parts to control indoor temperatures well.
The outdoor unit is the heart of your cooling system. It has important parts that work together to move heat from inside to outside. In commercial setups, these units handle bigger cooling tasks.
- Compressor: Pressurizes refrigerant and drives the heat transfer process
- Condenser Coil: Releases absorbed heat to the outside atmosphere
- Fan: Facilitates heat dissipation and airflow
- Refrigerant Lines: Connects indoor and outdoor units
“The outdoor unit is the heart of your cooling system, transforming warm indoor air into a comfortable living space.”
The refrigerant is key in this heat swap. It takes heat from indoor air and lets it out, making a cooling loop. Keeping these parts in good shape means better performance and energy use.
| Component | Function | Typical Lifespan |
|---|---|---|
| Compressor | Pressurize and circulate refrigerant | 10-15 years |
| Condenser Coil | Release heat to external environment | 15-20 years |
| Outdoor Fan | Facilitate heat dissipation | 10-15 years |
Knowing about your outdoor unit shows the amazing tech behind cooling homes. Whether it’s for your house or a big building, these parts work hard to keep things comfy and save energy.
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopInside Your HVAC System: Indoor Unit Elements
Your home’s HVAC system is made up of many parts working together. The indoor unit is key, housing important components for cooling and air flow.
Evaporator Coil: The Cooling Powerhouse
The evaporator coil is vital in your HVAC system. It pulls heat from indoor air, cooling your home in summer. But, these coils lose 5% to 10% efficiency each year if not kept clean.
- Absorbs indoor heat
- Facilitates cooling process
- Requires regular cleaning
Blower Motor: Circulating Comfort
Your blower motor moves air around your home. An unmaintained blower fan can use up to 30% of system energy. Regular checks boost your HVAC’s efficiency.
Air Filter Systems: Breathing Clean
Air filters keep your air clean by removing up to 99% of dust and pollen. But, clogged filters can cut system efficiency by 10% to 20%. So, it’s important to replace them often for your HVAC’s health.
| Component | Function | Maintenance Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Evaporator Coil | Heat Absorption | Annual Cleaning |
| Blower Motor | Air Circulation | Bi-Annual Inspection |
| Air Filter | Particle Filtration | Every 3 Months |
“Proper maintenance is the key to a long-lasting and efficient HVAC system.” – HVAC Professionals
By knowing about these components and keeping up with maintenance, you can make your cooling system last longer and work better.
HVAC Ductwork Design and Layout
Your home’s comfort relies on something often overlooked: the HVAC ductwork design. These complex networks spread conditioned air across your home. Knowing how they work can boost your home’s air quality and energy use.
Understanding HVAC airflow diagrams is key. They show important steps for ductwork to work well:
- Keep ducts straight to reduce air resistance
- Steer clear of tight turns and extra bends
- Make sure ducts are the right size for even air flow
- Seal ducts to stop air leaks
“Efficient ductwork is the circulatory system of your home’s climate control” – HVAC Engineering Professionals
Did you know about 20 percent of cool air can be lost in ductwork? This loss means higher bills and less system power. Experts in HVAC design look at many things to make systems better:
- They check airflow needs for each room
- They calculate the right duct sizes
- They pick the best materials
- They think about insulation
The best HVAC systems use smart design based on standards from ACCA and ASHRAE. This focus on airflow makes your home more comfy and energy-smart.
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopThermostat Operation and Control Systems
Your HVAC system’s brain is its thermostat. It manages temperature and comfort with great precision. Modern thermostats have evolved from simple devices to digital systems that save energy and are easy to use.
Today’s thermostats are amazing. They do more than just control temperature. You can control your home’s climate from anywhere with smartphone apps. They also track energy use and help you save on heating and cooling.
Smart Thermostat Integration
Smart thermostats are a big step up for your HVAC system. They offer features like:
- Remote temperature control via mobile apps
- Learning algorithms that adapt to your preferences
- Energy usage tracking and reporting
- Compatibility with voice assistants
Temperature Zoning Benefits
Temperature zoning lets you create comfort zones in your home. By dividing your space, you can:
- Reduce energy waste
- Minimize hot and cold spots
- Personalize temperature settings for different rooms
Programming for Efficiency
Programming your thermostat can save a lot of energy. Modern systems let you set schedules that adjust temperatures for you. For example, you can cool or heat your home when you return.
*”Smart thermostats can reduce energy costs by up to 15% annually”* – Energy Star
With advanced thermostats, you’re not just controlling temperature. You’re making your home more comfortable, efficient, and smart.
The Role of Refrigerants in HVAC Systems
Refrigerants are key to hvac heating and cooling systems. They help transfer heat and keep your home comfortable. These special fluids are vital for controlling your home’s temperature.
The refrigerant cycle shows how these substances change to cool or heat your space. The process has four main steps:
- Compression of low-pressure gas
- Heat release in the condenser
- Pressure reduction through expansion valve
- Heat absorption in the evaporator
“Refrigerants are the unsung heroes of indoor climate control, silently working to maintain your comfort.” – HVAC Engineering Experts
Modern refrigerants like R410A have replaced older, harmful ones. This shows big tech progress. Today’s systems are green and work well.
| Refrigerant Type | Environmental Impact | Energy Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| R410A | Low Global Warming Potentia | High Efficiency |
| R32 | Reduced Carbon Footprint | Excellent Performance |
It’s important to check refrigerant levels. EPA estimates show HVAC refrigerants cause 8% of global warming. Keeping your system maintained stops leaks and keeps it running right.
Learning about refrigerants helps you choose better for your HVAC. It’s about efficiency, lasting power, and being kind to the planet.
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopEnergy Efficiency and Performance Factors
Understanding energy efficiency in residential hvac maintenance can save you a lot of money. It also helps the environment. Your HVAC system is a big investment in your home’s comfort. It can save a lot of energy with smart choices and regular care.
Modern HVAC systems can greatly improve your home’s energy use. The average household spends over $2,200 a year on energy. Almost half of that goes to heating and cooling.
SEER Ratings Explained
SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings show how well your system cools. Here’s what you need to know:
- Higher SEER ratings mean better cooling efficiency
- New systems usually have SEER ratings from 13-22
- Choosing a high-efficiency system can cut energy use
Energy-Saving Features
Boost your hvac energy efficiency with these features:
- Variable-speed motors use less electricity
- Multi-stage compressors work better
- Smart thermostats can save about $180 a year
“Investing in energy efficiency is not just about saving money, but also reducing your carbon footprint.” – HVAC Energy Experts
Regular maintenance is key to keeping your system efficient. Change air filters every three months. Also, get professional inspections to keep your HVAC running well and last longer.
Common HVAC System Types and Configurations
Choosing the right HVAC system is key to your comfort and energy savings. Different setups fit various spaces, from homes to commercial buildings. Knowing these options helps you decide what’s best for your heating and cooling needs.
- Split Systems: Traditional setup with indoor and outdoor units
- Packaged Units: Compact systems ideal for smaller spaces
- Ductless HVAC systems: Flexible solutions for targeted cooling
- Hybrid Systems: Combining multiple energy sources for efficiency
Ductless HVAC systems are popular for their flexibility. They offer precise temperature control without the need for extensive ductwork. This makes them great for adding rooms, renovating, or spaces with limited setup options.
“The right HVAC system can reduce energy costs by up to 40% while improving overall comfort.” – HVAC Industry Research
Choosing a commercial HVAC system needs careful thought. Consider the building’s size, how it’s used, and specific temperature needs. Businesses often choose centralized systems for larger areas. These systems ensure consistent climate control across different zones.
| System Type | Best For | Energy Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Split Systems | Residential Homes | Moderate |
| Ductless Systems | Targeted Cooling | High |
| Packaged Units | Small Spaces | Low to Moderate |
When picking an HVAC system, think about space, budget, and energy costs over time. Each type has its own benefits that can meet your specific needs.
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopMaintaining Your HVAC System for Optimal Performance
Keeping your HVAC system in top shape is key for energy efficiency and avoiding expensive fixes. Regular upkeep extends your system’s life and keeps your home comfortable.
Proactive maintenance can stop up to 95% of system failures. A smart maintenance plan boosts your system’s performance and cuts energy use.
Seasonal Maintenance Checklist
- Replace air filters every 1-3 months
- Clean outdoor unit and remove debris
- Inspect refrigerant lines for leaks
- Check thermostat settings and calibration
- Clean indoor vents and registers
Regular upkeep can make your HVAC system 10-30% more energy-efficient. Simple steps like changing filters can cut energy use by 5-15%.
Professional Service Requirements
While DIY maintenance is good, professional help is essential. Certified techs can:
- Do detailed system checks
- Check electrical connections
- Lubricate moving parts
- Verify system refrigerant levels
- Assess overall system performance
Experts say you should get professional HVAC maintenance twice a year. This keeps your system running well and avoids sudden failures.
Regular maintenance can save you up to 30% on heating and cooling costs.
Conclusion
Learning about HVAC systems shows us the amazing world of heating and cooling. Your home’s comfort relies on a complex system that uses a lot of energy. Knowing how HVAC works helps you make smart choices to save energy and money.
Keeping your HVAC system in good shape is key to its long life. The U.S. Department of Energy says that regular care can boost efficiency by 5-15%. Simple steps like changing air filters and getting professional check-ups can make your system last longer and work better.
Being energy-efficient is more than saving money; it’s about living green. Smart thermostat settings and sealed ducts can cut energy bills by 10-30%. The ASHRAE standards keep pushing HVAC tech forward, keeping your system up to date for comfort and efficiency.
As HVAC tech gets better, knowing more about it is your biggest advantage. By using what you’ve learned, you can take care of and improve your heating and cooling systems for many years.

