Affiliate Disclosure
HVAC Guide Guys is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.
Can I Use Spray Foam Around HVAC Ducts? Did you know a 1-inch layer of cured closed-cell foam is recommended for metal ducts? It prevents unsightly and damaging condensation. Spray foam insulation is becoming more popular for HVAC systems. It’s important to know the safety guidelines and best practices for using it around your ductwork.
Spray foam insulation has many benefits, like better energy efficiency and moisture control. But, insulating your HVAC ducts with spray foam needs careful thought. You must consider application thickness, fire safety, and fresh air ventilation. In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about using spray foam around your HVAC system. This way, you can make the right choice and get the best results.

Key Takeaways
- Closed-cell spray foam is the recommended choice for HVAC duct insulation due to its superior moisture control and thermal performance.
- Proper application thickness and coverage calculations are crucial to ensure you use the right amount of spray foam.
- Ensuring adequate fresh air ventilation is essential in foam-insulated homes to maintain indoor air quality and system performance.
- Compliance with building codes and manufacturer requirements for HVAC systems in encapsulated attics is a must for safe and efficient operation.
- Careful attention to safety measures, including personal protective equipment and surface preparation, is necessary during the spray foam application process.
Table of Contents
Understanding Spray Foam Insulation for HVAC Systems
Spray foam insulation is a top pick for HVAC systems. It’s great for keeping temperatures steady and air tight. There are two main types: closed cell foam and open cell foam. Closed cell foam is best for HVAC ducts because it stops moisture, keeping systems running well.
Types of Spray Foam Available
Closed cell foam is denser and more rigid. It’s better at keeping out moisture and heat. Open cell foam is lighter and more open, good for other uses. But for ducts, closed cell foam is the way to go for better energy use.
Benefits of Using Spray Foam
Using spray foam in HVAC systems has many pluses. It seals ducts tight, stopping air leaks that waste energy. It also keeps temperatures even, making the HVAC system work less hard and saving on bills.
Temperature Requirements for Application
For spray foam to work best, apply it when it’s between 65°F and 85°F. This ensures it sets right and insulates well. Applying it outside this range can make it less effective, hurting energy use and temperature control.
Knowing about spray foam types and their perks helps homeowners and HVAC pros choose wisely. The right temperature and application are key for lasting energy savings and comfort.
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopCan I Use Spray Foam Around HVAC Ducts
Absolutely! Spray foam is a great choice for insulating HVAC ducts. But, it’s important to pick the right type of foam. For duct insulation, closed-cell spray foam is best because it stops moisture better than open-cell foam.
A 1-inch layer of cured closed-cell spray foam works well to stop condensation on metal HVAC ducts. It sticks to the duct surface, closing any gaps where moisture can form. This makes it a better choice than traditional wrap insulation.
The U.S. Department of Energy says that spraying air ducts with at least 1.5 inches of closed-cell spray foam can make a home Zero Energy. The right amount for wet foam is 1/3 inch, which grows to one inch when it dries.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Average Duct Leakage in U.S. Homes | 20-30% of airflow |
| Cost to Seal Ducts with Spray Foam | $2500 – $3000 for a 3-ton system |
| Cost to Seal Ducts with Mastic Paint | $1500 – $2500 per duct system |
| Average Cost to Modify Air Ducts | $495 per duct or vent |
When applying spray foam around HVAC ducts, choose closed-cell foam to avoid moisture problems. This foam seals tightly, boosting your HVAC system’s efficiency and cutting down on energy bills.
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopSafety Considerations When Using Spray Foam
When you work with spray foam insulation, safety comes first. You need the right personal protective equipment (PPE) to stay safe. This includes full-body coveralls, gloves, goggles, and a respirator or mask. These help prevent breathing in harmful fumes and particles.
Before you start, make sure the surface is ready. Cover up anything you don’t want the foam to stick to, like windows and electrical fixtures. This step ensures a clean finish and avoids damage.
Ventilation Requirements
Good ventilation is key during and after applying spray foam. Make sure the area is well-ventilated. You might need fans or open windows to get fresh air in. After the job is done, keep the area ventilated to clear out any remaining fumes.
In homes with spray foam, it’s important to have fresh air. The ASHRAE suggests changing the air every 4-5 hours for good indoor air quality. You can use mechanical systems or vents and openings to achieve this.
Required Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Full-body coveralls
- Gloves
- Goggles
- Respirator or mask
By following these safety tips and using the right PPE, you can have a safe and successful spray foam job. Always remember, safety is the most important thing when working with construction materials.
“Safety should always be the top priority when working with any construction materials.”
Closed Cell vs Open Cell Foam for Ductwork
Closed-cell spray foam is the best choice for insulating HVAC ducts. It has better moisture resistance than open-cell foam. This is key to stop condensation on metal ducts.
It also has a higher R-value per inch. This means it keeps the temperature and airflow in the ducts better. Closed-cell foam is the top pick for duct insulation.
Open-cell foam, on the other hand, can let moisture in. This can cause mold and mildew to grow. This can harm the ductwork and the air quality inside.
To keep your HVAC system working well, choose closed-cell spray foam. It’s the best for duct insulation.
| Characteristic | Closed-Cell Foam | Open-Cell Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent | Poor |
| R-Value per Inch | Higher | Lower |
| Condensation Risk | Low | High |
| Recommended for Ducts | Yes | No |
It’s important to use closed-cell spray foam right. Follow the maker’s rules for temperature and thickness. This helps prevent condensation and keeps your HVAC system working well.
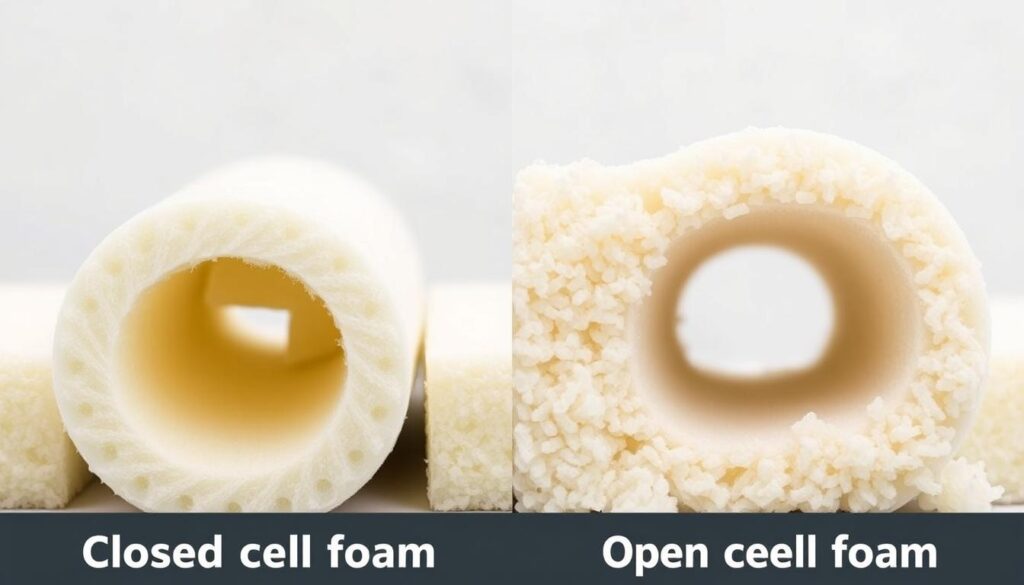
“Closed-cell foam is recommended for metal ducts that are ‘sweating,’ with a 1″ layer being able to prevent condensation from forming.”
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopProper Application Techniques for Duct Insulation
Insulating your HVAC ducts with spray foam needs the right techniques. From figuring out the coverage area to adjusting the spray pattern, each step is key. They help make sure your insulation works well and saves energy.
Coverage Calculations
First, figure out the area to cover in board-feet. A board-foot is a square foot thick one inch. For example, ducts that are 6 feet wide and 150 feet long cover 900 square feet.
The Foam it Green 602 kit can cover about 600 board-feet. So, you’ll need a bit more material to account for waste.
Application Thickness Guidelines
The foam should be 1/3 inch thick when wet. It will expand to 1 inch when dry. This thickness is best for insulation and meets industry standards.
The Foam it Green® Low-GWP Products are made for certain areas. This includes California, Colorado, and the Northeastern states.
Spray Pattern Recommendations
When spraying overhead, use the mixing nozzle alone. This lets you get closer and use a lighter touch. It helps prevent foam from bouncing off.
The Green indicator foam by Foam it Green changes color. This makes mixing easier and reduces waste.
“Each Foam it Green 602 comes with 10 mixing nozzles, so you have the tools you need to tackle even the most complex duct configurations.”
By using these best practices, you can ensure your HVAC ducts are well-insulated. This makes your insulation work smoothly and saves energy.
Fresh Air Ventilation Requirements in Foam-Insulated Systems
Proper ventilation is key in foam-insulated homes to keep the air clean. Spray foam makes homes very airtight. This can trap bad stuff like VOCs, water vapor, and odors.
To fix this, homes need mechanical ventilation systems. These systems bring in fresh air and get rid of stale, moist air.
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) says foam-insulated homes need about 100 CFM of air per 3,000 square feet. This means air should change every 4-5 hours. It’s important to tie ventilation to when people are home, not just when it’s hot or cold.
A whole-house ventilating dehumidifier can help. It mixes filtered fresh air into the home through the cooling ducts. This helps control the air exchange rate, ventilation control, and indoor air quality in foam-insulated systems.
| Air Change Rates | Typical Range |
|---|---|
| Older Homes | Over 1.0 ACH |
| Homes Built in the Last 20 Years | 0.35 to 0.70 ACH |
| Spray Foam Insulated Homes | 0.10 to 0.20 ACH |
Spray foam contractors should tell customers about the need for mechanical ventilation. They should have a plan for ventilation before starting any insulation work. This prevents air quality problems in tight homes and keeps occupants healthy and comfortable.
Impact on HVAC System Performance
Spray foam insulation boosts your HVAC system’s performance. It offers better thermal performance than old insulation methods. This means your home needs less energy to stay warm or cool.
With spray foam on the roof, your attic can be as comfortable as your living areas. This cuts down the work your HVAC system does. It makes your system more energy efficient.
Energy Efficiency Benefits
Spray foam insulation has many benefits for your HVAC system:
- It creates a tight seal that stops air leaks. This makes your HVAC system work less hard.
- It makes your home more energy-efficient. This lowers your heating and cooling bills.
- You can use smaller, more efficient HVAC systems. This is because the foam reduces the load on the system.
Load Calculation Considerations
Using spray foam changes how you size your HVAC system. It reduces the heat that gets through your home. This means you need a smaller HVAC system, saving energy and making your home more comfortable.
It’s important to work with skilled HVAC pros. They can figure out your home’s thermal performance. They’ll suggest the right system size to get the most out of spray foam insulation.
“Proper HVAC system sizing is crucial to achieving maximum energy efficiency and comfort in a home with spray foam insulation.”
Explore Our HVAC Shop
Looking for top-rated HVAC tools, parts, and accessories? Visit our shop and find the perfect solution for your needs.
Visit the ShopCommon Installation Mistakes to Avoid
Using spray foam insulation around HVAC ducts is crucial. It’s important to avoid common mistakes that can harm the system’s effectiveness and safety. One major issue is improper application temperature. Not keeping the tank at the right temperature can cause uneven and poor results.
Another mistake is inadequate surface preparation. It’s key to make sure surfaces are clean, dry, and free of dirt. Skipping this step can lead to gaps and voids, reducing the insulation’s performance.
- Ensure the tanks are at the recommended temperature using provided temperature strips.
- Avoid spraying on surfaces outside the 65°F-85°F temperature range, as this can impact the foam’s curing and expansion.
- Always use the recommended personal protective equipment (PPE) and follow the manufacturer’s application guidelines to ensure proper coverage and thickness.
Lastly, incorrect application thickness is another common error. Not applying the foam as recommended can result in poor insulation and performance issues. Always check the manufacturer’s specs and apply the foam correctly to get the best R-value and thermal performance.
| Common Mistake | Potential Impact | Prevention Measure |
|---|---|---|
| Improper tank temperature | Off-ratio spraying, inconsistent results | Use temperature strips to ensure tanks are at the proper temperature |
| Inadequate surface preparation | Poor adhesion, gaps, and voids in the insulation | Clean, dry, and prepare surfaces according to manufacturer’s guidelines |
| Incorrect application thickness | Insufficient insulation, compromised thermal performance | Apply spray foam at the recommended thickness to achieve the desired R-value |
By avoiding these common mistakes and taking the right precautions, you can ensure your spray foam insulation works well. This will improve energy efficiency, comfort, and the system’s long-term performance.

Maintenance and Long-Term Considerations
Spray foam insulation is known for lasting a long time and not settling or breaking down. But, to keep it working well, you need to check on it often. This is especially true for homes that are very well sealed with foam insulation.
Durability Factors
The way spray foam is made gives it great foam durability. It keeps moisture out and stops mold or mildew from growing. This helps keep the insulation strong, making sure your HVAC system works well for a long time.
Monitoring Requirements
- Keep an eye on the humidity inside your home to keep the air clean and prevent too much moisture.
- Think about getting a whole-house ventilating dehumidifier. It helps control humidity and keeps your home comfortable and healthy.
- Check the insulated ductwork regularly. This helps find any problems early and keeps everything running smoothly.
By being proactive with maintenance and checks, your spray foam insulation will keep performing well. It will keep your home energy-efficient for many years.
Conclusion
Spray foam insulation can make your HVAC ducts more efficient. It boosts HVAC efficiency and system performance. The closed-cell variety is especially good at keeping temperatures and humidity levels right.
Installing spray foam safely is key. You need the right gear and to make sure the area is well-ventilated. Also, watch out for insulation safety issues like fires and chemical risks.
With careful installation, spray foam can improve your HVAC system’s efficiency and comfort. This makes your home more energy-efficient and comfortable for everyone.

